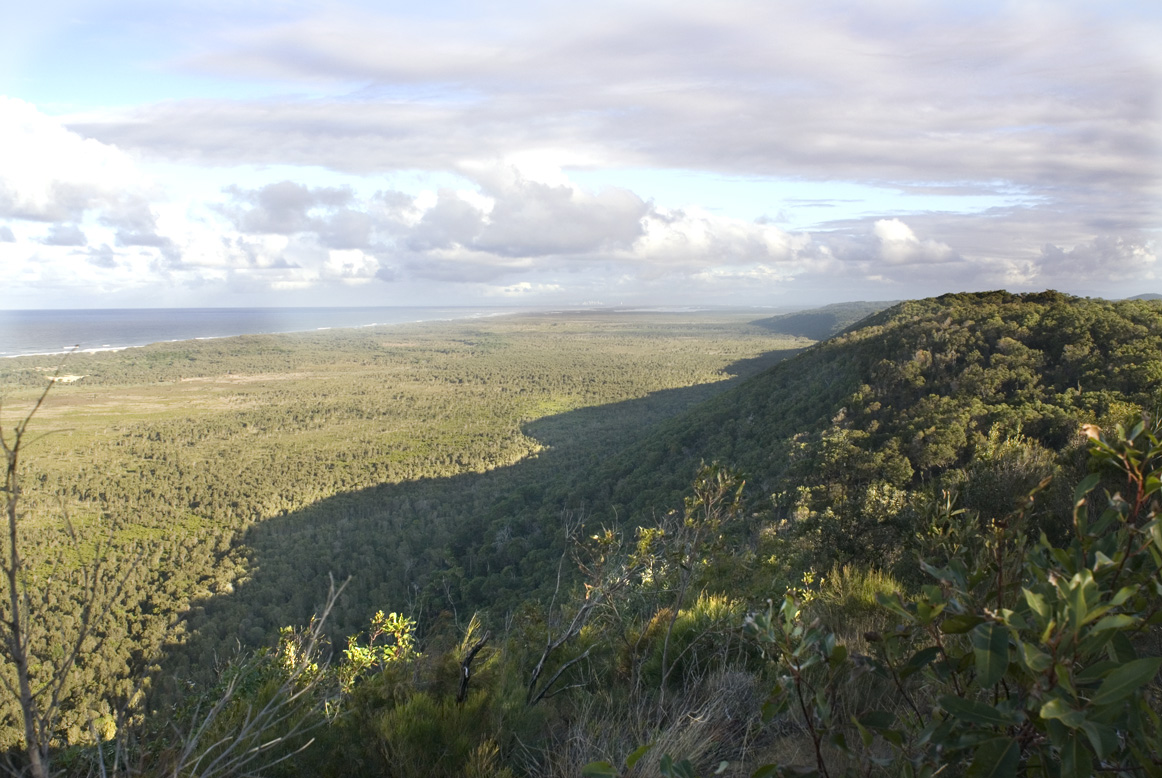
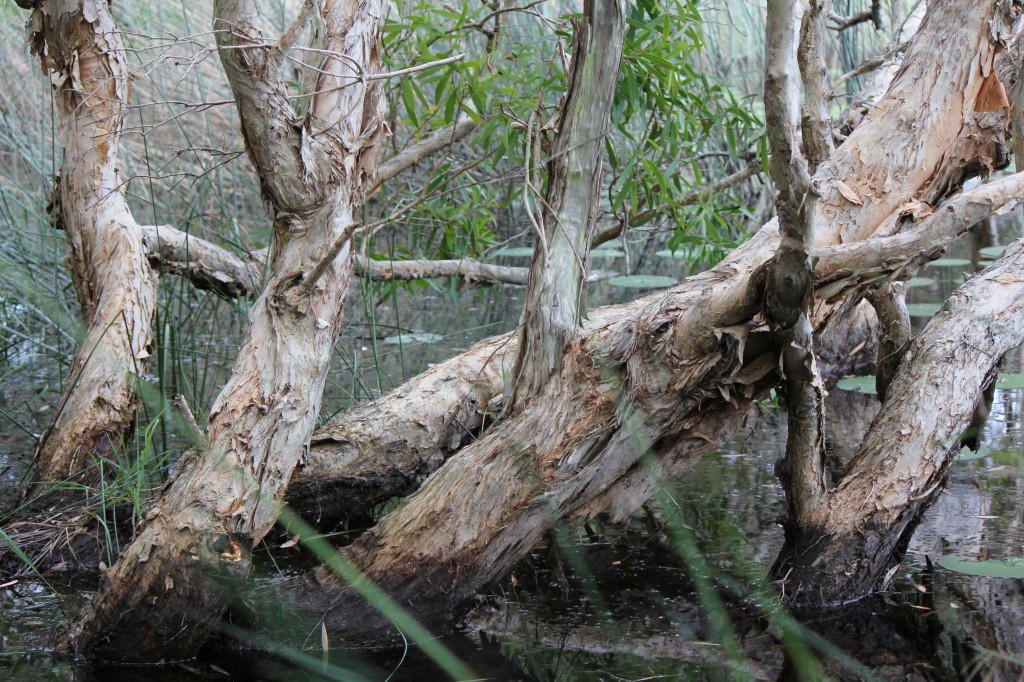
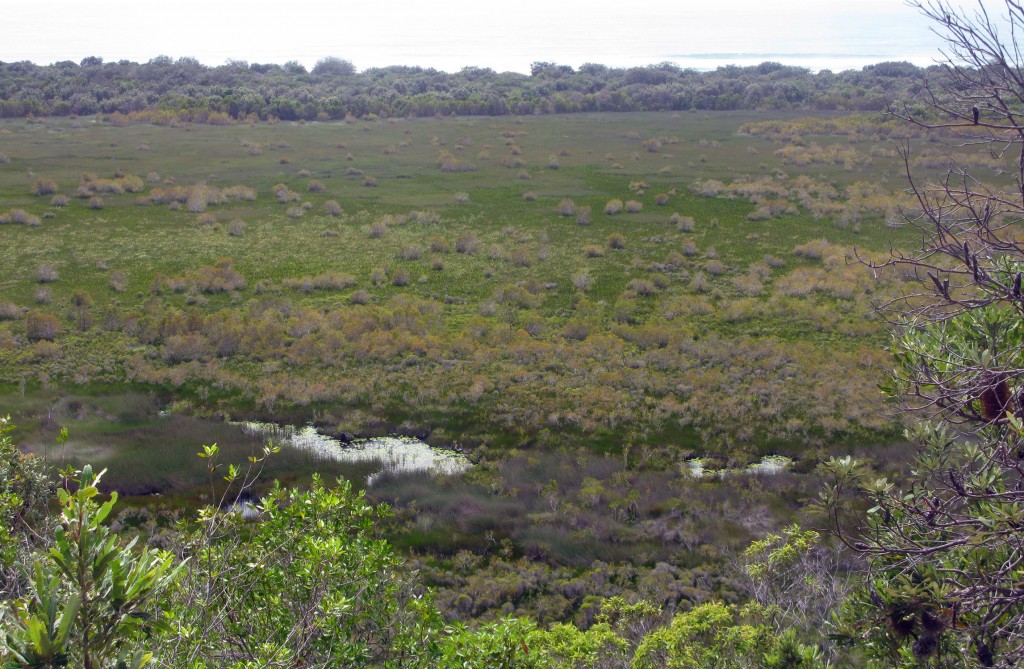
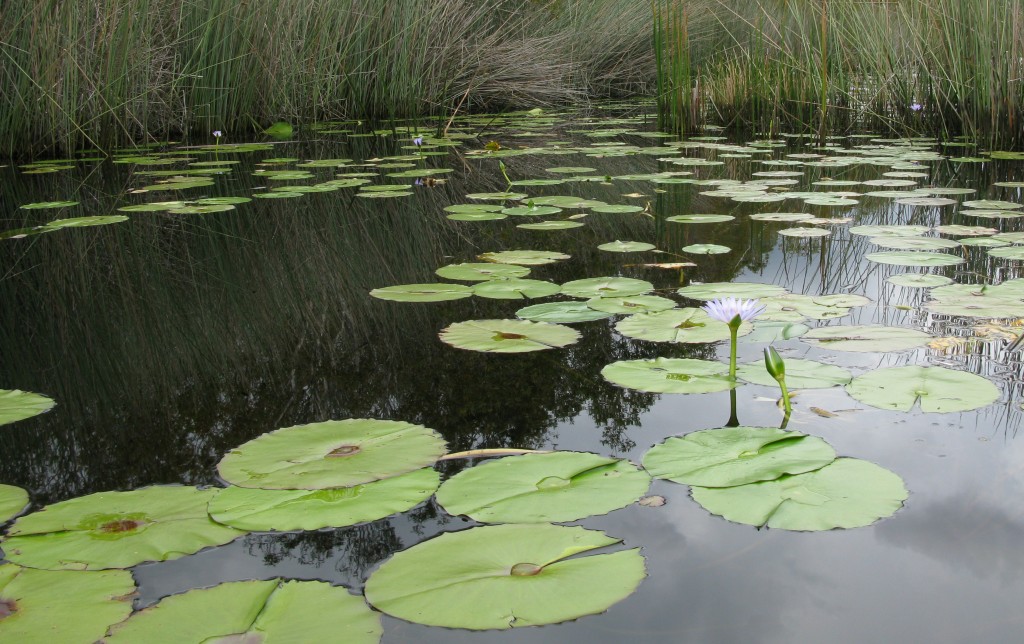
18 Mile Swamp wetland, North Stradbroke Island not protected
The 18 Mile Swamp is the largest of its kind in the world and is directly threatened by pollution from the nearby dredge sand mining at the ‘Enterprise’ mine. The area has been named NAREE BUDJONG DJARA NATIONAL PARK by indigenous people on the island who are engaged in its joint management with the Queensland State government and is home to many endangered rare species.
Not protected.
On 27th March 2011, Premier Anna Bligh announced parts of the 18 Mile Swamp wetland would be included as part of a staged national park using the rhetoric that 20% of North Stradbroke Island has now been protected. This internationally recognised RAMSAR listed wetland is a tract of land which could not be directly mined.
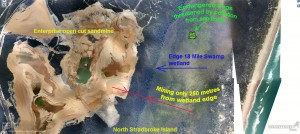
However the 18 Mile Swamp wetland remains threatened as the western sand escarpments (pictured right) and eastern shore (where the wetland is recharged with water) remain locked up within sandmining leases. Under Queensland State government policy the buffer distance between areas to be destroyed by open cut sandmining and RAMSAR declared wetland will be 20 meters at best. This Government policy threatens the 18 Mile Swamp wetland and its habitat for endangered species with pollution.
Enterprise open cut sandmine encroaching on the 18 Mile Swamp wetland.
Map on left shows extensive sandmining operations occur within 250 meters of the 18 Mile swamp wetland. This sandmining increases the risk of pollution entering the wetland habitat of nationally recognised endangered frog species.
Fragile and unknown hydrology – threatened by sand mining
As with most complex natural systems there is insufficient information on the hydrology (movement, distribution and quality of water) regarding the 18 Mile Swamp and much of Straddie’s groundwater systems. The groundwater is difficult to monitor because of the dynamic character of salt and freshwater interfaces. It has not yet been properly determined how either groundwater extraction or the potential subsequent saltwater intrusion will directly affect the swamp ecosystem and indirectly affect the quality of the water in the surrounding connected ecosystems and the major body of the aquifer.
For this reason all groups considering the swamp as a resource (mining and the Redland City Council) have been running the gauntlet over the years. The mining process requires large amounts of water. This water has been obtained from the swamp and its connecting groundwater systems. The miners use spears to monitor water levels around the mines but with the deep dredge mining depths below the water table, draining and flooding have occurred in areas surrounding mines on a number of occasions. The drained Lake Kounpee due to sand mining to the West of the Island is an example.
The 18 Mile Swamp could still experience negative effects with deep dredge mining continuing close by at Enterprise.
For many years, the Redland water supply has also depended on extraction from the swamp of water for domestic water supply purposes. The risks of water extraction are ongoing. The precautionary principle really needs to come into play in the care of this new National Park.
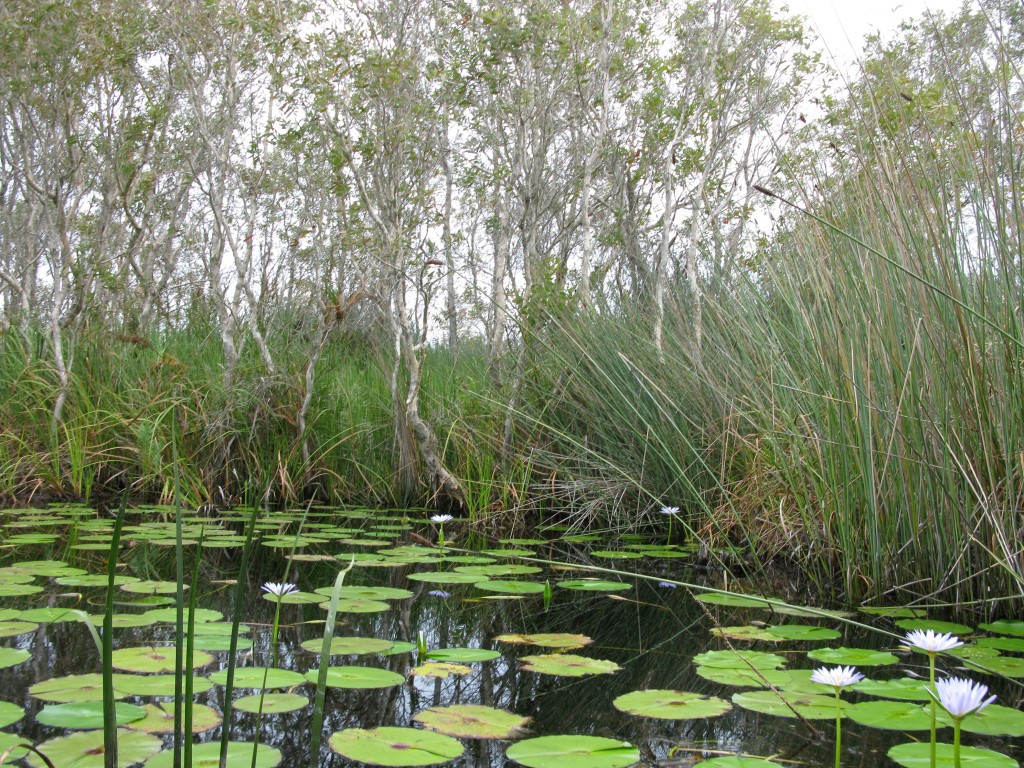
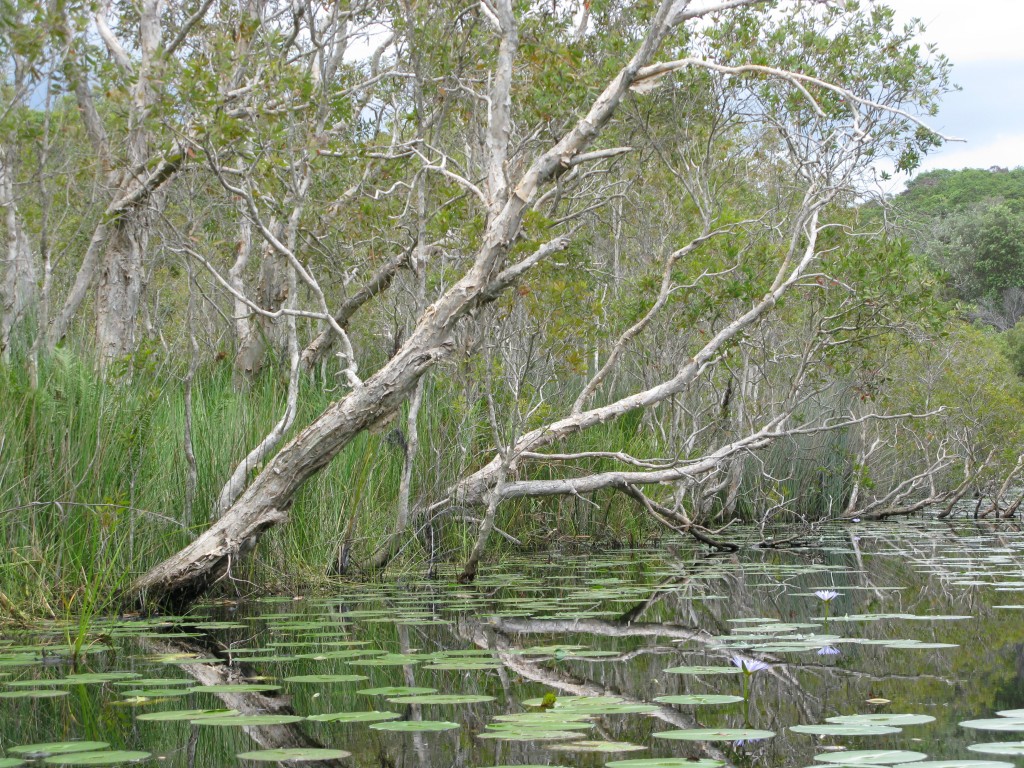
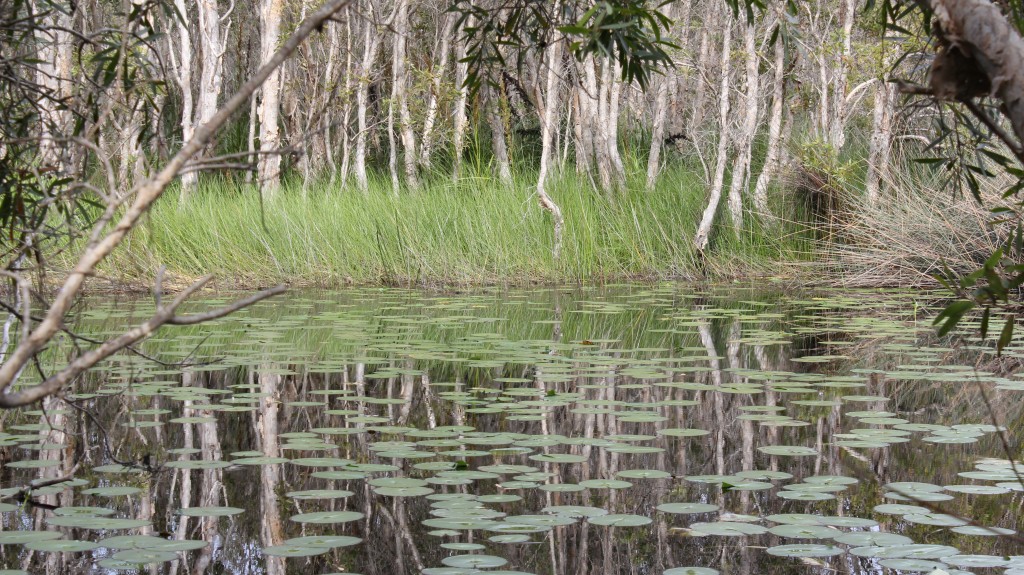
Vegetation in the swamp
Extending from about 3.5 km south of Point Lookout to Swan Bay this great area of dense vegetation looks inviting from afar. Closer contact, however, reveals an environment challenging for human contact. Since its formation about 6,000 years ago it remains relatively untouched by mining and disturbance to the peat forming process. This occurs below the surface mat of tea-tree, reeds, ghania (a tall razor-sharp grass) and ferns as the sea level in this locality was up to 7 metres below the present level approximately 8,000 years ago and up to 1 to 1.5 metres above 6,000-6,500 years ago.
Formation of the swamp
It has been determined that this back barrier swamp formed during a less than 1 metre fall in the sea level since. This allowed a new beach to form eastwards and thus prevented the westward movement of sea water. The swamp, which receives its water from the island dunes, contains Freshwater Creek which is barely discernible in much of the Northern section. It is surprisingly deep where it enters the sea water conditions of the mangrove and palm swamp adjacent to the shallow sea of Swan Bay to the south.
In the last sixty years there has been a noticeable increase in tea-tree and weeds (groundsel, etc) in lieu of reeds in the southern and mid sections of the swamp. This may be caused by an increase in salt-water ingress from Swan Bay with a slight increase in sea level or the extraction of fresh water for the mainland. The peat in the fresh water area is about 10 metres deep and consists of 4 metres of fibrous peat overlying 6 metres of an older gel-like material of embryonic coal. Hydrogen sulphide gas is evident in the anaerobic decomposition of the peat. This gas is also more noticeable where sea-water enters in the southern area.
Fires in the swamp
Periodic fires have influenced the swamp environment but the indigenous people may have used this as a hunting device. The swamp wallaby, which may have been hunted, is a fine red-golden coloured animal unique to the North and South Stradbroke Islands. In dry periods fire can reduce the swamp to ash in a matter of days. The recovery of the vegetation, however, indicates that fire adaptation is a characteristic of the present dense vegetation.
Fire may also have been used by the original inhabitants to allow easier access to the beach from the inland. There are middens within the swamp on isolated and rare sand-rises which indicate old aboriginal pathways. Mosquitoes are abundant, especially at night in the southern section, in spite of the presence of fish in all areas which feed on their larvae. This, as well as the disease inherent in the anaerobic bacteria, is another deterrent to human ingress.

Ship-wreck in the swamp
The 18 Mile Swamp wetland may also contain a mystery ship-wreck described by Fred Campbell of Amity in a manuscript handed to Tom Welsby before he died in 1898. He thought that it was the wreck of Pamphlett and Finnegan’s ship, positioned he described as 4 miles north of Swan Bay and a mile in from the sea.
This is, of course, well into the swamp. All fire-blackened remains above waterlevel have disappeared since 1954. Enough descriptions exist to describe this ship as heavily built, oak-framed, sheathed in Muntz metal and containing copper and iron bolts and rivets. It has been described as 30 yards long, aligned as a beeline north south with the bow facing north. The use of Muntz metal and copper defines a possible time of its construction. Another time bracket is that it was an apparently unknown wreck after Moreton Bay was settled. Fred Campbell gained knowledge of it from the tribal elders of
Moongalba and Amity and wrote that the first white men the aborigines had ever seen were Pamphlett and Finnegan, the discoverers of the Brisbane River. Later, it was Welsby himself who researched this and wrote that they, with Parsons, had been wrecked on Moreton Island. This suggests that the mystery ship was abandoned further south by its crew at sea and may have been a drifting wreck washed ashore onto the beach to await an intense cyclonic storm or a tsunami to carry it into the swamp. Of the over 6,000 known Australian ship-wrecks only one appears to satisfy these conditions.
After the Second World War a timber causeway of two heavy hardwood planks supported by crossbeams on driven hardwood posts provided access to the Blue Lake from the beach. A small rowing boat was also provided at a deep section, presumably Freshwater Creek, too wide to span by the planks. It was thought that the army had constructed this for either recreation or defence. Alas, it is no more.
The sand mining company in the late 1950’s had a dredge working the lease covering the beach sand dunes. To convey the concentrate to the large facilities at Dunwich a high moving aerial ropeway with moving hoppers led directly across the swamp to the present sand-loading facility. Steel towers to support the pulleys feeding the steel cables were erected across the island at intervals including three in the dredged swamp. Remains of these may still exist in the water where they were collapsed when the whole affair became obsolete. The swamp under the ropeway was dredged and cleared as access for a small motorised barge.
The Keyholes – lakes, inaccessible due to destructive sand mining
At the northern end of the swamp the Keyholes are clear freshwater lakes, delightful for canoeing, but are now close to the Yarraman mine and, therefore, not accessible to the public as it is a prohibited mining area.